Gadolinium chelates
These are the most commonly used contrast agents in MRI. Gadolinium has a predominant T1 effect and will produce an enhancement in T1.
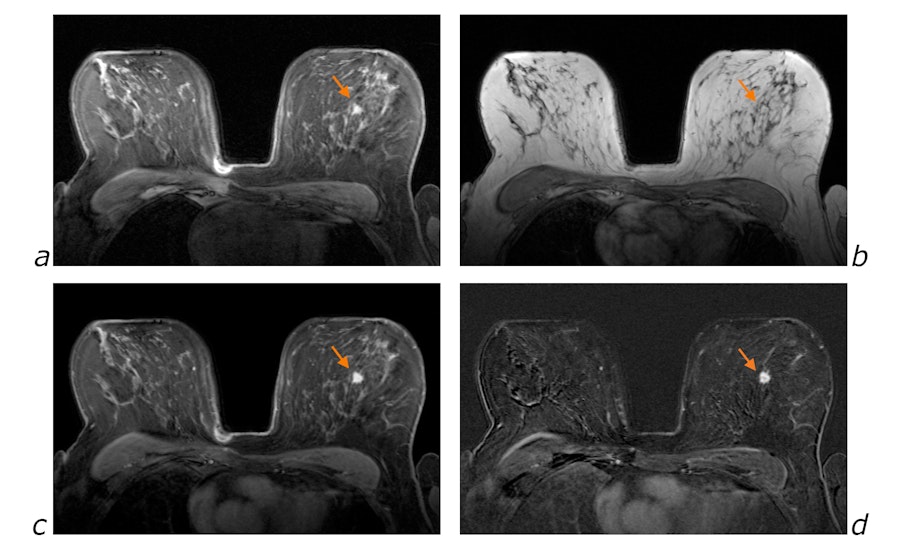
Fat signal suppression and enhancement after Gadolinium injection in breast MRI
a. T1 weighted axial slice with fat saturation, before Gadolinium injection
b. T1 weighted axial slice after Gadolinium injection, without fat saturation
c. T1 weighted axial slice after Gadolinium injection, with fat saturation
d. Subtraction of images before and after injection (images a. and c.)
Brand names
- Dotarem® / Artirem® (Gd-DOTA)
- Eovist® (Gd-EOB-DTPA)
- Multihance® (Gd-BOPTA)
- Magnevist® (Gd-DTPA) and Omniscan® (Gd-DTPA-BMA) (reassessment of the risk benefit)
Enhancement examples
Pharmacological and pharmacokinetic data about Gadolinium chelates
Toxicity in the free state: Administration in chelate form, of variable chemical structure (linear or macrocyclic) depending on the molecule.
Pharmacokinetics similar to that of iodized contrast agents:
- Biodistribution that is initially intra-vascular with a rapid passage to the interstitial sector
- Does not pass the healthy blood-brain barrier
- Elimination by renal route.
- Gd-BOPTA and Gd-EOB-DTPA: liver-specific properties with excretion in the bile.
T2 effect of Gadolinium chelates
At weak concentration, the T2 effect of Gadolinium chelates is negligible compared to the T1 effects.
The T2 effect predominates and is only visible at high concentrations, for example in the bladder after renal excretion.
Perfusion MRI also exploits the magnetic susceptibility effect due to the first intravascular passage of a concentrated bolus of Gadolinium chelate, responsible for a drop in the T2 and T2* signal.
Intravascular contrast agents
New high vascular remanence contrast agents are now available (Gadofosveset Vasovist®). They reversibly bind to the macromolecules present in blood circulation (albumin), which modifies their pharmacokinetics. They remain in blood vessels longer, improving imaging of the vascular system using magnetic resonance angiography.
In research, contrast agents based on Gadolinium chelates bound to macromolecules (polyethylene glycol derivatives) are being studied. Too bulky to pass through the normal endothelium they are able to better characterize cancerous lesions, which are accompanied by increased permeability of the vascular wall.
Contraindications and Adverse effects
Contraindications
- Allergy
- Pregnancy (relative contraindication by precautionary principle, to be assessed according to the risk/benefit ratio)
Adverse effects
- Nausea, headache, taste alteration, paresthesia
- Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis
Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis
Cutaneous fibrosing impairment with possible visceral extension in the days or months following an injection of Gadolinium chelates, in patients with an inflammatory background, and with severe renal failure and liver transplantation as risk factors.
Brain deposits
It was shown that the injection of gadolinium causes deposits in the brain tissue. However, linear contrast agents causes greater gadolinium retention than macrocyclic contrast products.
